TETRAMETHYLTHIURAM MONOSULFIDE
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
97-74-5
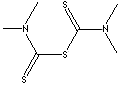
208.38
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
yellow to brownish powder
MELTING POINT
SOLUBILITY IN WATER
>200 C
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Health: 2, Flammability: 1, Reactivity: 0
150 C
APPLICATIONS
Tetramethylthiuram monosulfide (TMTM) is used as a secondary accelerator with thiazoles, guanidines, sulfenamides and dithiocarbamates. It is used as a fungicide, and insecticide.
APPEARANCE
yellow to brownish powder
ASSAY
95.0% min
MELTING POINT
101 C min
SIEVE ANALYSIS
0.1% max (+ 150 µm)
HEAT LOSS
0.5% max
OIL ADDITIVE
1.0 - 2.0%
ASH
0.5% max
Accelerator, in the rubber industry, is any of numerous chemical substances added with a curing agent to speed the vulcanization of rubber to enhance physical characteristics, e.g., strength, elasticity, and resistance to solvents, and to render it impervious to moderate heat and cold at lower temperatures. Accelerators are the most important organic materials containing sulfur and nitrogen, especially derivatives of benzothiazole. The most popular accelerators are delayed-action sulphenamides, thiazoles, thiuram sulphides, dithocarbamates and guanidines. Part or all of the sulphur may be replaced by a sulphur donor such as a thiuram disulphide. The sulphur produces cross-links between some of the solid bonds in the molecule. Vulcanization can also be accomplished with certain peroxides, gamma radiation, and several other organic compounds. The principal classes of peroxide crosslinking agents are dialkyl and diaralkyl peroxides, peroxyketals and peroxyesters. Other vulcanizing agents include amines for the crosslinking of fluorocarbon rubbers, metal oxides for chlorine-containing rubbers (notably zinc oxide for chloroprene rubber) and phenol-formaldehyde resins for the production of heat-resistant butyl rubber vulcanizates.
PRICE